2018-03-22 21:41
@AndrewTseng 分享的一个小玩意 JFinal使用技巧-Enjoy导出XLS
2018-03-21 22:37
不贴代码 .. 能猜出来才怪.... 提问题时还是需要站在别人的角度看下吧 ..
我猜有可能是你 tomcat 配的有问题 :
JFinal 部署在 Tomcat 下推荐方法
"记住第一点,永远不要将项目放在 TOMCAT_HOME/webapps 目录下面"
2018-03-14 23:10
方法一
拦截器
inv.getController().getResponse().addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");//指定域名
方法二
1, JFinal的Controller返回的时候如下:
这里的content就是我的Json字符串
renderJson("innerSignCallBack(" + content + ")");//跨域的请求,jsonp
2, 页面的Ajax如下:
var url = 'http://xxx.com/getJson';
$.ajax({
type : "get", //必须get,不填也行
url : url,
dataType : "jsonp",
jsonp:'innerSignCallBack', //服务器端获取回调函数名的key
jsonpCallback:'innerSignCallBack', //回调函数名
success:function(data) { //成功
alert('成功')
},
error : function(msg) {//失败
alert('失败');
}
});
2018-03-14 17:12
@麻言 你没有咨询波总吗?或者看 jfinal-club项目里session功能实现:
cache 接管了request Session ,这样你就可以随意操作用户的“session ”了,
踢用户线下功能,也只是一个remove的事。
* session 存放在数据库中,并引入 cache 中间层,优点如下:
* 1:简单且高性能
* 2:支持分布式与集群
* 3:支持服务器断电和重启
* 4:支持 tomcat、jetty 等运行容器重启
2018-03-14 13:40
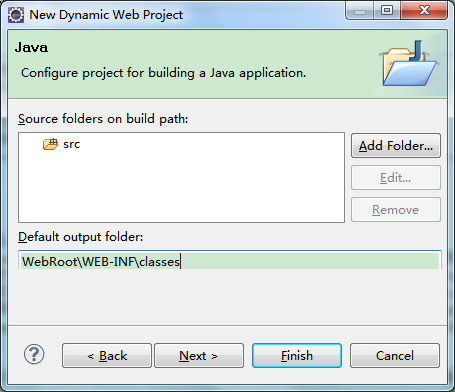
@syso 看手册内容 3、修改Default Output Folder,推荐输入WebRoot\WEB-INF\classes
特别注意:此处的 Default out folder必须要与 WebRoot\WEB-INF\classes 目录完全一致才可以使用 JFinal 集成的 Jetty 来启动项目。