这月新晋级奶爸了,代码写的都少了哈哈~~~
如题,当我们业务有涉及到复杂的数据组装和计算时,我都喜欢使用传统的JavaBean装载业务数据。里面可以写一些该业务的专有运算方法,又不会污染基础Model类,后续阅读业务代码也会清晰一点。
废话不多说,上石马:
import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.Record;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class RecordToBean {
public static <T> T to(Record r, Class<T> clazz) {
try {
T ret = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = Introspector.getBeanInfo(clazz, null)//
.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) {
Object value = getValue(r, pd);
pd.getWriteMethod().invoke(ret, value);
}
return ret;
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static <T> List<T> to(List<Record> list, Class<T> clazz) {
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = Introspector.getBeanInfo(clazz, null)//
.getPropertyDescriptors();
List<T> ret = new ArrayList<>(list.size());
for (Record r : list) {
T obj = constructor.newInstance();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) {
Object value = getValue(r, pd);
pd.getWriteMethod().invoke(obj, value);
}
ret.add(obj);
}
return ret;
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static Object getValue(Record r, PropertyDescriptor pd) {
String key = pd.getName();
Class<?> type = pd.getPropertyType();
if (String.class.equals(type)){
return r.getStr(key);
}
if (Integer.class.equals(type)){
return r.getInt(key);
}
if (Boolean.class.equals(type)){
return r.getBoolean(key);
}
if (java.math.BigDecimal.class.equals(type)){
return r.getBigDecimal(key);
}
if (Long.class.equals(type)){
return r.getLong(key);
}
if (java.math.BigInteger.class.equals(type)){
return r.getBigInteger(key);
}
if (java.util.Date.class.equals(type)){
return r.getDate(key);
}
if (Double.class.equals(type)){
return r.getDouble(key);
}
if (Float.class.equals(type)){
return r.getFloat(key);
}
if (java.time.LocalDateTime.class.equals(type)){
return r.getLocalDateTime(key);
}
if (Short.class.equals(type)){
return r.getShort(key);
}
if (Byte.class.equals(type)){
return r.getByte(key);
}
if (Number.class.equals(type)){
return r.getNumber(key);
}
return r.get(key);
}
}测试:
public static class MyBean{
private String a;
public void setA(String a) {
this.a = a;
}
private BigDecimal b;
public void setB(BigDecimal b) {
this.b = b;
}
//get...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyBean{" +
"a='" + a + '\'' +
", b=" + b +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Record r = new Record();
r.set("a", "A");
r.set("b", "888");
MyBean t = RecordToBean.to(r, MyBean.class);
System.out.println(t);
List<Record> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(r);
list.add(r);
List<MyBean> rs = RecordToBean.to(list, MyBean.class);
System.out.println(rs);
}结果:
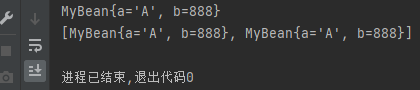
非常方便!
常见用法: List<Record> list = Db.templateByString(sql, Kv.create()).find(); List<MyBean> rs = RecordToBean.to(list, MyBean.class);



